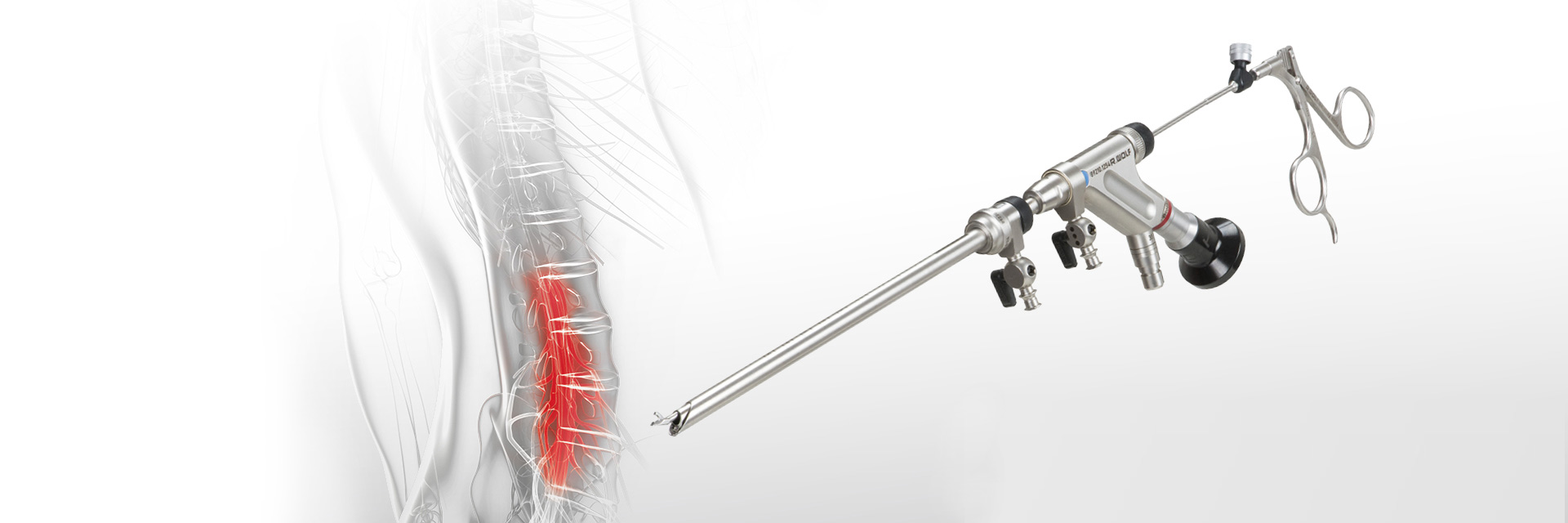
Over a period of decades, the specialists at RIWOspine and Richard Wolf have been working together with physicians and hospitals throughout the world with the goal of developing innovative methods and products for minimally invasive surgery and pain therapy.
Today, the latest technologies and innovations, such as 4K camera system, precise and tissue-conserving radiofrequency application, TipControl instruments and flow-controlled irrigation system are also available for endoscopic spine surgery and pain therapy.
RIWOspine products meet the highest standards of quality, safety and surgical use.
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
VERTEBRIS lumbar |
VERTEBRIS stenosis |
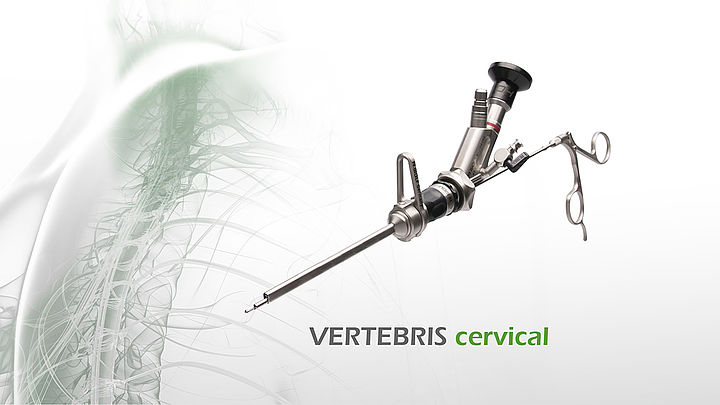
VERTEBRIS cervical |
Equipment Unit |
VERTEBRIS lumbar
The VERTEBRIS lumbar instrument set is designed for full-endoscopic decompression of the lumbar and thoracic spine. Typical indications include herniated discs, spinal cysts and spinal canal stenoses. The following approaches can be done full-endoscopically:
- Transforaminal
- Extraforaminal
- Interlaminar
The excellent optical properties of VERTEBRIS diskoscopes are the basis for intraoperative visualization and guide special instruments into the intraoperative area. The universal setting of the instruments also makes it possible to expand the indications by gradually adding new compoents.
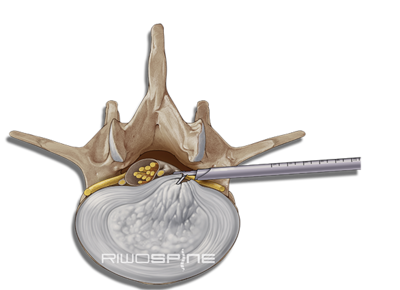 |
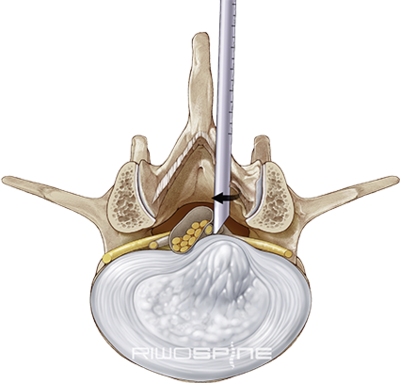
Trans-/ extraforaminal techniqueThe trans- or extraforaminal technique uses the intervertebral foramen as access to the pathology. The access to the intervertebral disk through the intervertebral foramen (transforaminal) or pedicle (extraforaminal) is placed under X-ray control with a puncture cannula. After dilation and insertion of the working sleeve, further surgery is performed through the diskoscopes under continuous irrigation with high-resolution endoscopic imaging. |
 |
VERTEBRIS transforaminal
|
 |
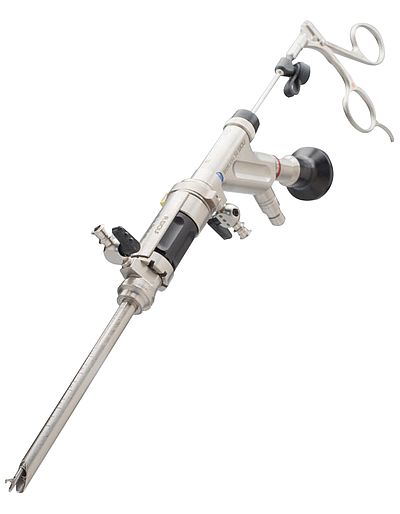
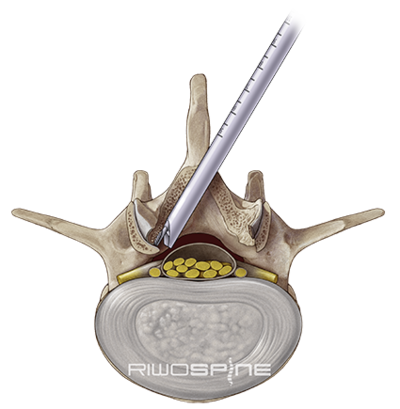
Interlaminar techniqueIn interlaminar surgery, the access to the spinal canal is done via the posterior interlaminar window. The dilator is guided directly to the flavum ligament with a dilator without prior puncture. After placing the working sleeve over the dilator, the operation is performed through the high-resolution diskoscope under continuous irrigation. The functionality of the components of the access system and the instruments are precisely coordinated and allow to pass through the ligamentum flavum and the nerve root with minimal traumatization. |
VERTEBRIS interlaminar
|
 |
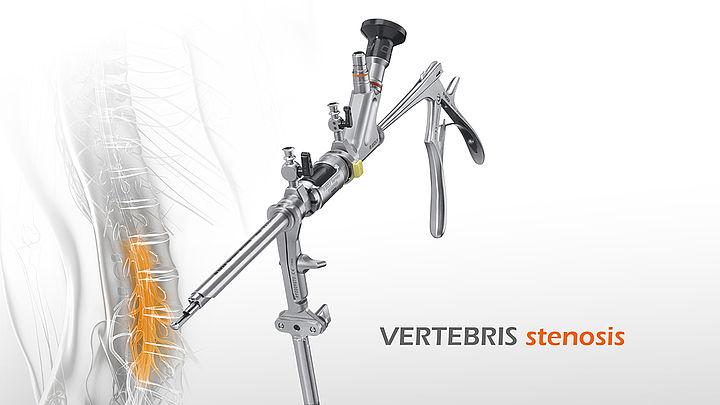
VERTEBRIS stenosis
Richard Wolf, working together with pioneering spine surgeons, was the first company to develop a standardized approach to full-endoscopic decompression of lumbar spinal canal stenosis. The Central Stenosis instrument set represents a true milestone of innovation and advancement in spine endoscopy.
A larger telescope with a correspondingly larger intra-endoscope working channel and larger, stronger instruments were necessary for the more extensive bone and ligament resection necessitated in this operation. The VERTEBRIS stenosis Instrument Set is complemented by the universal motor system and a variety of rigid and articulated burrs.
 |
Interlaminar techniqueIn interlaminar surgery, the access to the spinal canal is done via the posterior interlaminar window. The dilator is guided directly to the flavum ligament with a dilator without prior puncture. After placing the working sleeve over the dilator, the operation is performed through the high-resolution diskoscope under continuous irrigation. The functionality of the components of the access system and the instruments are precisely coordinated. It even allows to pass through the ligamentum flavum and the nerve root with minimal traumatization. |
VERTEBRIS stenosis
|
 |
 |
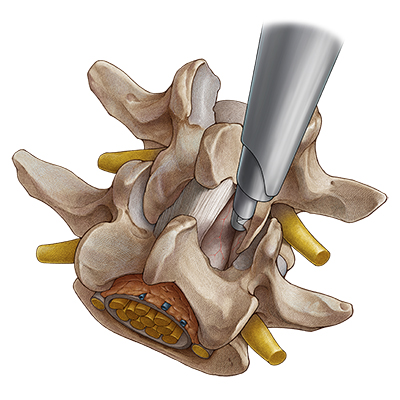
Ipsilateral decompression on one sideAfter the access has been created, the bony structures are exposed. It may be helpful to start decompression at the caudal end of the descending facet. Depending on the pathology, decompression is then commenced with resection of parts of the medial descending facet, the cranial and caudal lamina, and the ligamentum flavum. The extent of decompression generally continues cranially at least until the tip of the ascending facet and caudally to half of the pedicle. The medial portions of the ascending facet and the ligamentum flavum are then resected until sufficient decompression of the neural structures can be clearly seen - cranially, caudally and laterally. In the case of a central stenosis, the ligamentum flavum generally needs to be resected medially to the midline. Finally, it may be necessary to remove protruding annulus parts and osteophytes in the ventral epidural space. |
 |
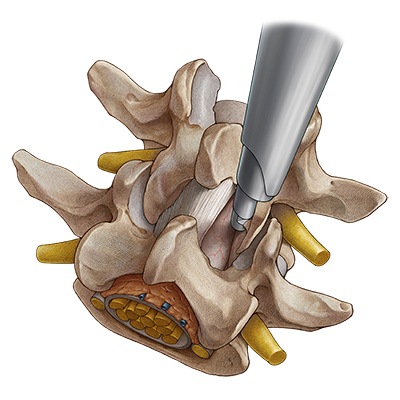
Contralateral decompression in over-the-top techniqueIf bilateral symptoms occur with a central stenosis, a unilateral approach is carried out with "over-the-top" access using the undercutting technique to the opposite side. For this purpose, bone in the ventral area of the spinous process is resected until the contralateral side can be accessed dorsally up to the dura of the spinal cord. If possible, the ligamentum flavum is initially left in place to protect the dura and bony decompression is again carried out by laminotomy and partial facetectomy. The ligamentum flavum is then completely resected. Finally, the contralateral recess needs to be extended. The decompression is completed when the dura and the spinal nerves have been clearly decompressed. |
VERTEBRIS cervical
The main indications for cervical full-endoscopic operations are "soft" spinal disc herniations with radicular symptoms. Two basic instrument sets are available for use in the cervical spine. They are designed specifically for the special anatomical requirements of an anterior approach and a posterior approach.
The visual quality, and the special design of the instrument sets, allow for a quality of endoscopic surgery equivalent to lumbar procedures. The customized instruments and standardized techniques are important enablers for the success of these innovative surgical methods used on the cervical spine.
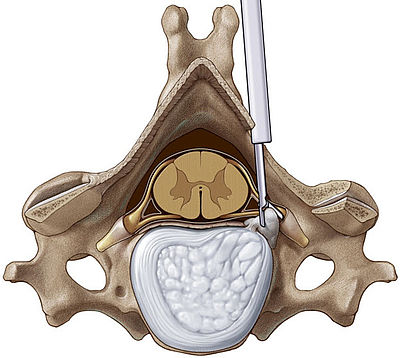 |
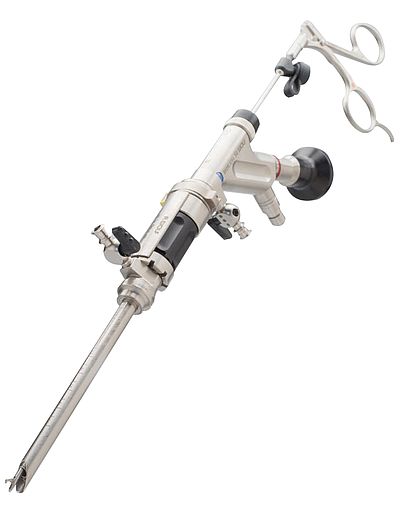
Posterior techniqueThe posterior cervical instrument system includes a specially designed instrument set and a well defined, repeatable, technique for the posterior approach to the cervical spinal canal. The instrumentation includes bone burrs that give the surgeon the ability to perform bone resection under visualization in the area of the foramen, the uncinate process or the posterior edge of the spinal column. |
VERTEBRIS cervical posterior
|
 |
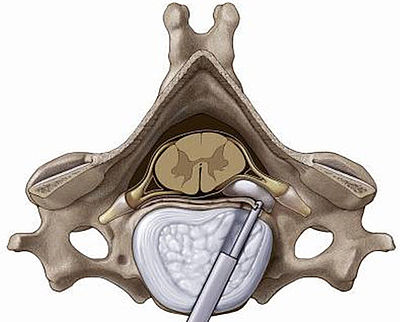 |
Anterior techniqueHerniations presenting with their main portion located medially to the lateral edge of the spinal cord are regarded as indications for an anterior approach to the cervical spine. The anterior cervical system includes a custom designed dilator-sleeve system which interfaces with a unique cervical endoscope, as well as specialized instrumentation, to provided excellent access to the posterior disc area. The full-endoscopic anterior cervical approach provides a significantly less traumatic alternative to conventional surgery. |
VERTEBRIS cervical anterior
|
 |
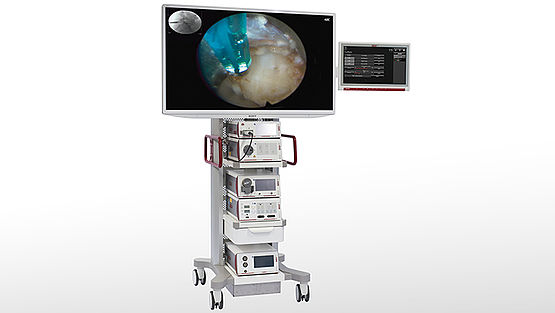
RIWOspine Equipment Unit
The complete device network for full endoscopic spinal surgery guarantees highest functionality and safety in the OR. The 55" 4K camera system for spine surgery is the centerpiece of the unit and marks a new standard in endoscopic visualization. All devices required for endoscopic spine procedures are positioned in a space-saving and user-friendly manner.
The integrated core nova OR system impresses with its simple and ergonomically directly accessible control unit. The status information of all connected devices is visible at all times and guarantees the necessary overview to surgeons and OR staff. Altogether this makes operating considerably easier.
Endocam Logic 4KENDOCAM pictures cast a spell over the viewer and offer a brilliant visual experience in endoscopy. Clear and razor sharp images in realistic colors enable the recognition of smallest structures with a detailed spatial depth effect. Optimized high performance for your OR.
|
 |
 |
core nova Device OperationIntuitive and ergonomic due to direct access and overview |
|
Integrated in core nova Optimized high performance for your OR
|
|
Devices
 |
Radiofreqency surgical systemThe Radioblator RF4 Radiofrequency Generator with a working frequency of 4 MHz is the centerpiece of an effective tissue-preserving coagulation system. By comparison with standard radiofrequency devices supplied commercially in the marketplace, the electricity frequency of the Radioblator RF4 is approximately 10 times higher. |
 |
Burr & Shaver systemThe expansion of indications for full-endoscopic techniques to treat conditions ranging from disk herniations to bony spinal canal stenosis requires efficient bony and soft-tissue resection. The powerful PowerSpeed AS1, M5 motor and High-speed handpieces, and associated burrs and resectors meet this requirement. |
 |
Fluid managmentFLUID CONTROL Arthro is a new pump system for arthroscopy and full-endoscopic spine surgery. The particular strength of this system consists of a combination of high performance and cost-effective overall concept. The new software and technical enhancements make FLUID CONTROL Arthro ideal for interventional and surgical procedures. |
 |
Endoscopic imagingWe define a new quality of imaging in full-endoscopic spine surgery. With Richard Wolf camera systems, very small and fine structures can be clearly identified and differentiated. |